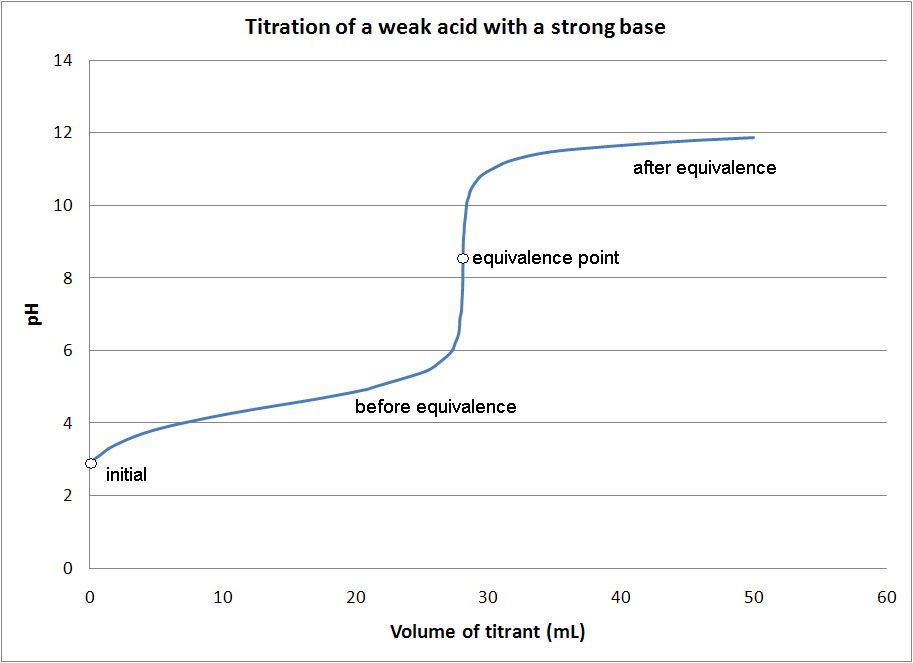
Volume Titration Equivalence Point . technically, the equivalence point is where the titration curve exhibits an inflection point. At this point the curve has the steepest slope. The only thing in solution is its conjugate. a titration is a volumetric technique in which a solution of one reactant (the titrant) is added to a solution of a second reactant (the. Sorting out some confusing terms. Our titrant will always be a strong acid or base (in this course). the higher molarity of the acid compared to the base in this case means that a smaller volume of the acid is required to reach the. the equivalence point of a titration is the point at which 'chemically equivalent' amounts of acid and base have been mixed. the equivalence point of a titration.
from exoliotyy.blob.core.windows.net
Our titrant will always be a strong acid or base (in this course). technically, the equivalence point is where the titration curve exhibits an inflection point. the equivalence point of a titration is the point at which 'chemically equivalent' amounts of acid and base have been mixed. The only thing in solution is its conjugate. the higher molarity of the acid compared to the base in this case means that a smaller volume of the acid is required to reach the. Sorting out some confusing terms. the equivalence point of a titration. At this point the curve has the steepest slope. a titration is a volumetric technique in which a solution of one reactant (the titrant) is added to a solution of a second reactant (the.
Equivalence Point Titration Example at Daniel Hoggard blog
Volume Titration Equivalence Point the higher molarity of the acid compared to the base in this case means that a smaller volume of the acid is required to reach the. technically, the equivalence point is where the titration curve exhibits an inflection point. Sorting out some confusing terms. a titration is a volumetric technique in which a solution of one reactant (the titrant) is added to a solution of a second reactant (the. the higher molarity of the acid compared to the base in this case means that a smaller volume of the acid is required to reach the. At this point the curve has the steepest slope. the equivalence point of a titration. the equivalence point of a titration is the point at which 'chemically equivalent' amounts of acid and base have been mixed. The only thing in solution is its conjugate. Our titrant will always be a strong acid or base (in this course).
From www.numerade.com
SOLVED Match the provided labels to the appropriate point on the Volume Titration Equivalence Point At this point the curve has the steepest slope. Our titrant will always be a strong acid or base (in this course). the equivalence point of a titration. technically, the equivalence point is where the titration curve exhibits an inflection point. The only thing in solution is its conjugate. a titration is a volumetric technique in which. Volume Titration Equivalence Point.
From quizspattering.z21.web.core.windows.net
How To Find Equivalence Point Volume Volume Titration Equivalence Point a titration is a volumetric technique in which a solution of one reactant (the titrant) is added to a solution of a second reactant (the. At this point the curve has the steepest slope. Our titrant will always be a strong acid or base (in this course). technically, the equivalence point is where the titration curve exhibits an. Volume Titration Equivalence Point.
From chemwiki.ucdavis.edu
Titration of a Weak Base with a Strong Acid Chemwiki Volume Titration Equivalence Point the higher molarity of the acid compared to the base in this case means that a smaller volume of the acid is required to reach the. Our titrant will always be a strong acid or base (in this course). a titration is a volumetric technique in which a solution of one reactant (the titrant) is added to a. Volume Titration Equivalence Point.
From www.vrogue.co
Ph Indicators Titration Curves Teaching Resources vrogue.co Volume Titration Equivalence Point Our titrant will always be a strong acid or base (in this course). a titration is a volumetric technique in which a solution of one reactant (the titrant) is added to a solution of a second reactant (the. At this point the curve has the steepest slope. the equivalence point of a titration is the point at which. Volume Titration Equivalence Point.
From www.researchgate.net
Titration curve of acetic acid at 30 °C (Ve = equivalence volume Volume Titration Equivalence Point the higher molarity of the acid compared to the base in this case means that a smaller volume of the acid is required to reach the. the equivalence point of a titration is the point at which 'chemically equivalent' amounts of acid and base have been mixed. technically, the equivalence point is where the titration curve exhibits. Volume Titration Equivalence Point.
From www.youtube.com
How to Calculate the Volume of Titrant Needed to Reach Equivalence Volume Titration Equivalence Point Our titrant will always be a strong acid or base (in this course). the equivalence point of a titration is the point at which 'chemically equivalent' amounts of acid and base have been mixed. the equivalence point of a titration. At this point the curve has the steepest slope. technically, the equivalence point is where the titration. Volume Titration Equivalence Point.
From www.chemistrystudent.com
Titration Curves (ALevel) ChemistryStudent Volume Titration Equivalence Point Our titrant will always be a strong acid or base (in this course). a titration is a volumetric technique in which a solution of one reactant (the titrant) is added to a solution of a second reactant (the. The only thing in solution is its conjugate. the equivalence point of a titration. Sorting out some confusing terms. At. Volume Titration Equivalence Point.
From www.youtube.com
Finding equivalence point for Monoprotic acid YouTube Volume Titration Equivalence Point a titration is a volumetric technique in which a solution of one reactant (the titrant) is added to a solution of a second reactant (the. the higher molarity of the acid compared to the base in this case means that a smaller volume of the acid is required to reach the. the equivalence point of a titration.. Volume Titration Equivalence Point.
From www.numerade.com
SOLVED Text Fill in the following table using your graph Titrant Volume Titration Equivalence Point Our titrant will always be a strong acid or base (in this course). technically, the equivalence point is where the titration curve exhibits an inflection point. the equivalence point of a titration. The only thing in solution is its conjugate. a titration is a volumetric technique in which a solution of one reactant (the titrant) is added. Volume Titration Equivalence Point.
From exolnazbp.blob.core.windows.net
A Titration Reached The Equivalence Point When 16.1 Ml at Amber Holmes blog Volume Titration Equivalence Point a titration is a volumetric technique in which a solution of one reactant (the titrant) is added to a solution of a second reactant (the. the higher molarity of the acid compared to the base in this case means that a smaller volume of the acid is required to reach the. Sorting out some confusing terms. Our titrant. Volume Titration Equivalence Point.
From chemistrytalk.org
Titration Curves & Equivalence Point Calculations ChemTalk Volume Titration Equivalence Point the higher molarity of the acid compared to the base in this case means that a smaller volume of the acid is required to reach the. The only thing in solution is its conjugate. Sorting out some confusing terms. technically, the equivalence point is where the titration curve exhibits an inflection point. At this point the curve has. Volume Titration Equivalence Point.
From www.expii.com
What Is a Titration Curve? — Overview & Parts Expii Volume Titration Equivalence Point the equivalence point of a titration is the point at which 'chemically equivalent' amounts of acid and base have been mixed. Sorting out some confusing terms. the equivalence point of a titration. technically, the equivalence point is where the titration curve exhibits an inflection point. The only thing in solution is its conjugate. At this point the. Volume Titration Equivalence Point.
From studymarxianism.z21.web.core.windows.net
How To Find Equivalence Point Volume Titration Equivalence Point Our titrant will always be a strong acid or base (in this course). the higher molarity of the acid compared to the base in this case means that a smaller volume of the acid is required to reach the. the equivalence point of a titration is the point at which 'chemically equivalent' amounts of acid and base have. Volume Titration Equivalence Point.
From www.numerade.com
SOLVED Total Volume of the Solution (mL) What' Point Along Titration Volume Titration Equivalence Point a titration is a volumetric technique in which a solution of one reactant (the titrant) is added to a solution of a second reactant (the. technically, the equivalence point is where the titration curve exhibits an inflection point. the equivalence point of a titration is the point at which 'chemically equivalent' amounts of acid and base have. Volume Titration Equivalence Point.
From www.numerade.com
SOLVED Equivalence Point pH volume titrant (mL) Figure P1 Volume Titration Equivalence Point technically, the equivalence point is where the titration curve exhibits an inflection point. the higher molarity of the acid compared to the base in this case means that a smaller volume of the acid is required to reach the. the equivalence point of a titration. the equivalence point of a titration is the point at which. Volume Titration Equivalence Point.
From quizspattering.z21.web.core.windows.net
How To Find Equivalence Point Volume Volume Titration Equivalence Point The only thing in solution is its conjugate. Sorting out some confusing terms. technically, the equivalence point is where the titration curve exhibits an inflection point. the equivalence point of a titration. the higher molarity of the acid compared to the base in this case means that a smaller volume of the acid is required to reach. Volume Titration Equivalence Point.
From www.numerade.com
SOLVED Q4 Titrations 3 Points The figure below refers to a titration Volume Titration Equivalence Point At this point the curve has the steepest slope. technically, the equivalence point is where the titration curve exhibits an inflection point. Sorting out some confusing terms. the higher molarity of the acid compared to the base in this case means that a smaller volume of the acid is required to reach the. the equivalence point of. Volume Titration Equivalence Point.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT How to Interpret Titration Curves PowerPoint Presentation ID225155 Volume Titration Equivalence Point The only thing in solution is its conjugate. At this point the curve has the steepest slope. Sorting out some confusing terms. the equivalence point of a titration. technically, the equivalence point is where the titration curve exhibits an inflection point. the higher molarity of the acid compared to the base in this case means that a. Volume Titration Equivalence Point.